NinjaDoH: A Censorship-Resistant Moving Target DoH Server
Using Hyperscalers and IPNS
Abstract
We introduce NinjaDoH, a novel DNS over HTTPS (DoH) protocol that leverages the InterPlanetary Name System (IPNS), along with public cloud infrastructure, to create a censorship-resistant moving target DoH service. NinjaDoH is specifically designed to evade traditional censorship methods that involve blocking DoH servers by IP addresses or domains by continually altering the server’s network identifiers, significantly increasing the complexity of effectively censoring NinjaDoH traffic without disruption of other web traffic. We also present an analysis that quantifies the DNS query latency and financial costs of running our implementation of this protocol as a service. Further tests assess the ability of NinjaDoH to elude detection mechanisms, including both commercial firewall products and advanced machine learning-based detection systems. The results broadly support NinjaDoH’s efficacy as a robust, moving target DNS solution that can ensure continuous and secure internet access in environments with heavy DNS-based censorship.
Key contributions
- Moving-target DoH design & implementation using hyperscaler IP agility and IPNS to distribute the latest server endpoint and query path.
- Performance evaluation showing low-latency DNS resolution comparable to public DoH providers (and dramatically faster than DNS-over-Tor).
- Censorship-resistance evaluation demonstrating evasion of common firewall blocklist techniques and reduced effectiveness of baseline ML detectors.
- Cost analysis indicating the prototype deployment can be run for approximately $23.55/month (configuration-dependent).
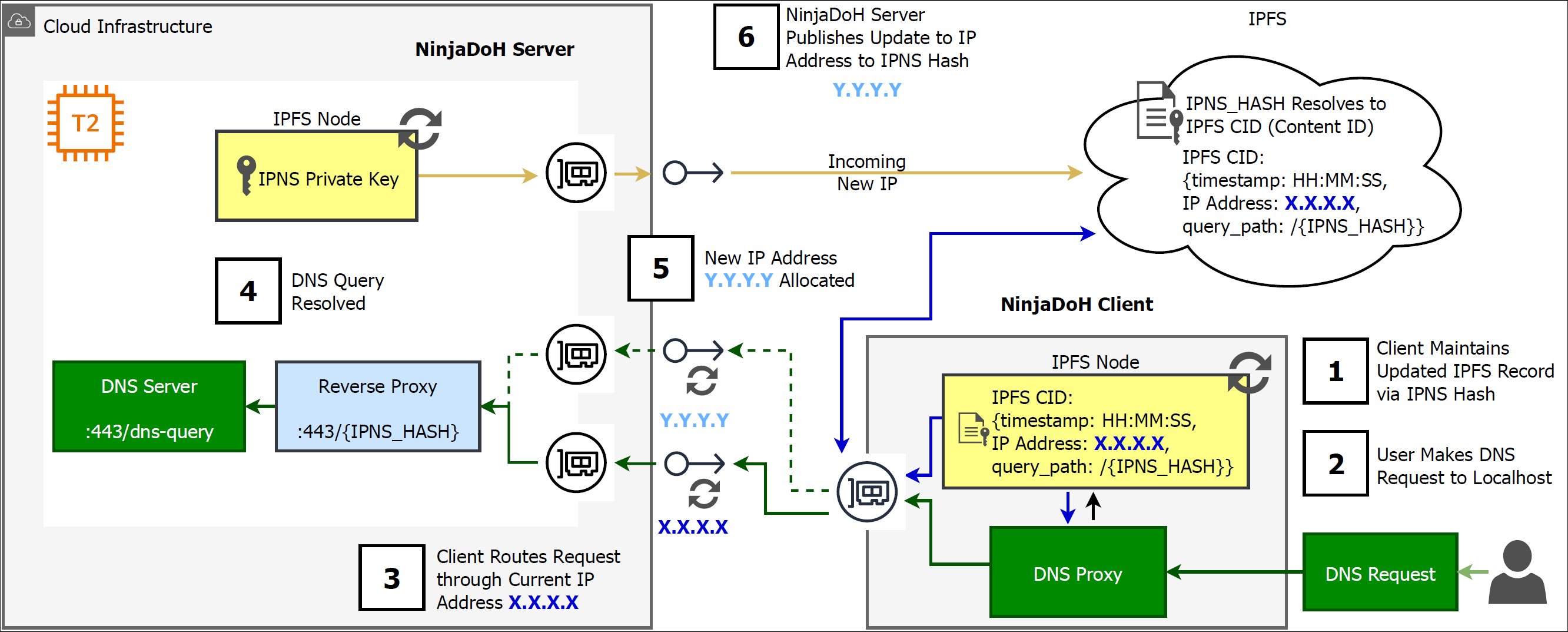
System overview
NinjaDoH is built around a moving target defense: the server rotates public IP addresses on hyperscaler infrastructure, while a decentralized “control plane” (IPNS/IPFS) publishes the latest server IP address and a randomized DoH query path. The client resolves the IPNS record, updates a local DNS proxy, and routes DNS queries over HTTPS to the current server endpoint—preserving compatibility with existing browsers and applications.
Problem: Encryption hides the content, but not the traffic pattern. NinjaDoH focuses on defeating the patterns censors rely on: static lists, fingerprints, and long-lived flow signatures.
Control plane: IPNS/IPFS
Clients learn the latest server IP + query path via an IPNS name resolving to IPFS content (CID).
Data plane: HTTPS (DoH)
DNS queries blend into normal port 443 traffic while avoiding standard DoH fingerprints (e.g., fixed /dns-query paths).
Zero-downtime IP rotation
Overlapping IP assignments (“the ladder”) allow smooth handoff while clients refresh endpoints.
Fast certificate updates
A private CA enables rapid certificate issuance compatible with frequent IP rotations.
Results
See the paper for full experimental methodology, confidence intervals, and threat model assumptions.
Slides
Tip: scroll horizontally (trackpad/swipe) or use the arrows to navigate. The download button above opens the full PDF (zoom/search).
BibTeX
@inproceedings{Seidenberger2026NinjaDoH,
title = {NinjaDoH: A Censorship-Resistant Moving Target DoH Server Using Hyperscalers and IPNS},
author = {Seidenberger, Scott and Beret, Marc and Wijewickrama, Raveen and Jadliwala, Murtuza and Maiti, Anindya},
booktitle = {Workshop on Measurements, Attacks, and Defenses for the Web (MADWeb)},
year = {2026},
address = {San Diego, CA, USA},
month = {Feb},
doi = {10.14722/madweb.2026.23006},
url = {https://dx.doi.org/10.14722/madweb.2026.23006}
}